Brief
Linked List Basics
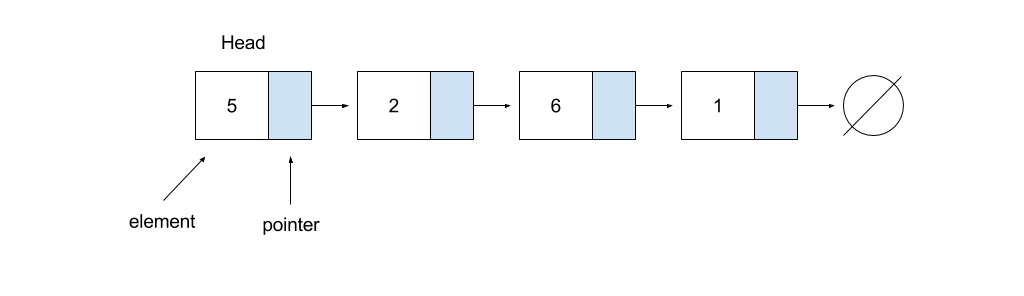
A linked list is a collection of nodes that together form a linear ordering. The “head” node of the list represents the front, while the node that points to NULL represents the end of the list.
A node consists of an element and a pointer:
- The element stores data
- The pointer points to the next node in the list
Visual Representation
This particular linked list consists of four nodes. Notice that each node has two components; an element and a pointer. The head node contains the value 5 and points to the node that contains the value 2. The end node contains the value 1 and points to NULL.
Implementation
The following code is the implementation of a simple linked list. The code consists of a struct that represents the nodes of the linked list and an insertFront function to insert elements into the list.
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next; // Pointer to the next node in list.
};
void insertFront(Node* &head, int element) {
Node* newNode = new Node; // Allocates a new node.
newNode->data = element; // Assigns a value for data in newNode.
newNode->next = head; // The node head points to is now the node that
// comes after newNode.
head = newNode; // NewNode is now the head.
}Node consists of two members: an integer variable named data and a pointer to Node. These two components make up the core fundamentals of a linked list.
The insertFront function takes in a reference to a Node pointer that points the the head of the list and an integer you want to insert into the list.
The insertFront function first allocates a new node, it then assigns a value to that node it allocated. The pointer of that new node is then assigned to the current head of the list (this makes the connection between the new node and the list). The head pointer of the list is then assigned to point to the new node.
Here is some sample code that creates an empty linked list and inserts 8 into the list:
int main() {
Node *head = NULL; // Creates a pointer to the front of the list.
insertFront(head, 8); // Inserts 8 at the front of the list.
}